우연히 보게된 노마드 코더(Nomad Coders)의 유튜브.
파이썬 코드만가지고 JS, React, NextJS 인터랙티브 웹앱을 만들어주는 프레임워크가 나타났단다.
최근 정말 많은 주목을 받고 있는 오픈소스 프로젝트인 것은 분명한 것 같다.
Pynecone: The easiest way to build web apps.
Completely customizable. All Pynecone components are fully customizable. Change the colors, fonts, and styles to match your project. Styling guide ->
pynecone.io
발음이 같은 'pinecone'을 상징하는 솔방울을 로고로 사용하고 있다 ^^
공식 웹사이트도 Pynecone을 사용해서 만들었다고 한다.
왠지 Unix is Not Unix 같은 느낌인데!? 아닌가?! ^^
Pynecone은 파이썬으로 작성한 코드를
React/NextJS로 컴파일을 하는 방식이기에 성능이 뛰어나며 그래서 node를 필요로 하고 있다.
보다 더 나은 성능을 위해 node를 bun으로 교체하는 작업을 하고 있지만
아직 100% 호환성을 보장하지 못하기에 당분간은 node를 계속 필요로 할 것이라고 한다.
서두가 길었다.
이제 직접 한 번 사용해보자.
이하 과정은 다음 링크의 내용을 따라갔다.
- https://pynecone.io/docs/getting-started/installation
0. PoC Environment
- 이하 과정을 진행한 환경은 Ubuntu 20.04 64bit Desktop 이다.
2. Prerequisites
- Python 3.7+
- NodeJS 12.22.0+
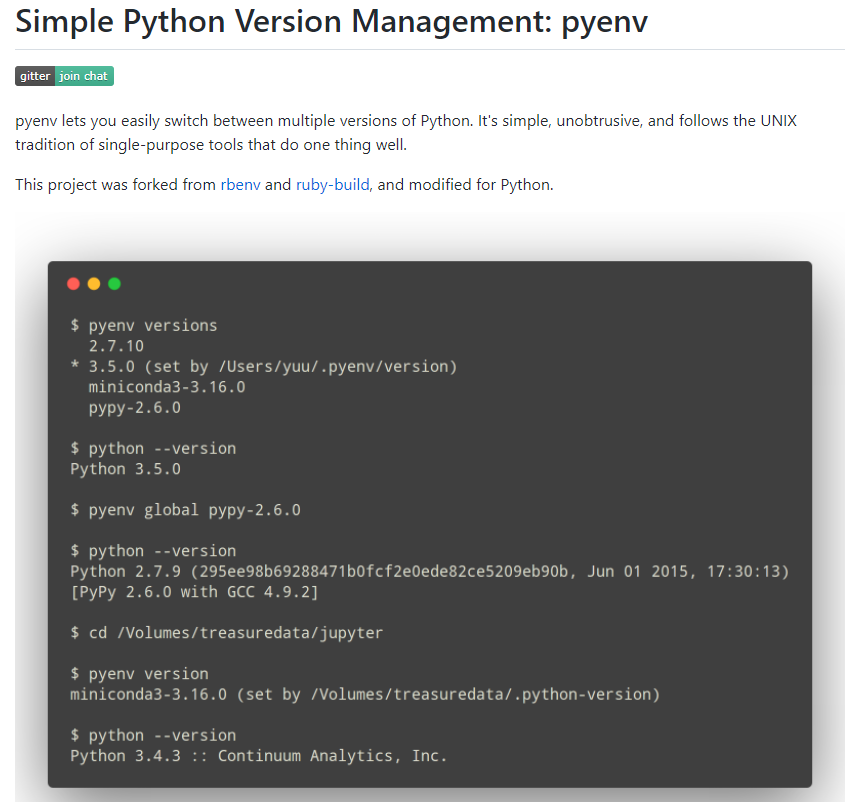
① Python 여러 버전을 관리할 수 있는 pyenv 기반으로 설치해보자.
. https://www.whatwant.com/entry/pyenv
. 설치한 버전은 다음과 같이 했다.
- v3.8.16
② node 설치도 여러 버전을 관리할 수 있는 nvm 기반으로 설치를 진행해보자.
. https://www.whatwant.com/entry/npm
. 설치한 버전은 다음과 같이 했다.
- v18.15.0 (Latest LTS: Hydrogen)
3. Virtual Environment
- Optional 이라지만, 사실 필수이지 않을까 싶다.
| ❯ cd ./workdir ❯ python -m venv .venv ❯ source .venv/bin/activate |
4. Installing
- 이제 pynecone 설치하면 된다!
| ❯ pip install pynecone |
5. Create a Project
- 일단 프로젝트 생성하는 방법부터 알아보자.
| ❯ mkdir my_app_name ❯ cd my_app_name ❯ pc init |
6. Run the App
- 일단 한 번 띄워보자.
| ❯ pc run |
- 브라우저로 확인해보자.

7. Edit
- 본문을 살짝 살펴보자.
| ❯ nano my_app_name/my_app_name.py |
- 눈꼽만큼 변경해보자.
| """Welcome to Pynecone! This file outlines the steps to create a basic app.""" from pcconfig import config import pynecone as pc docs_url = "https://pynecone.io/docs/getting-started/introduction" filename = f"{config.app_name}/{config.app_name}.py" class State(pc.State): """The app state.""" pass def index() -> pc.Component: return pc.center( pc.vstack( pc.heading("Welcome to WHATWANT!", font_size="2em"), pc.box("Get started by editing ", pc.code(filename, font_size="1em")), pc.link( "Check out our docs!", href=docs_url, border="0.1em solid", padding="0.5em", border_radius="0.5em", _hover={ "color": "rgb(107,99,246)", }, ), spacing="1.5em", font_size="2em", ), padding_top="10%", ) # Add state and page to the app. app = pc.App(state=State) app.add_page(index) app.compile() |
- 포트도 변경하고, debug log도 찍어보자.
| ❯ pc run --port 8282 --loglevel debug |
- http://localhost:8282/

8. Fast Refresh
- Pynecone은 실시간으로 변경 사항이 반영된다.
- 웹브라우저가 띄워져 있는 상황에서, 다른 터미널로 파일을 수정해보자.
| ❯ nano my_app_name/my_app_name.py |
- 파일을 수정한 뒤, 저장을 하면 조금 있다가 브라우저에 자동으로 페이지 내용이 변경된다.
일단 여기까지 살짝 맛만 봤고
시간이 나면 다음 단계로 넘어가보겠다. (시간이 날까?! ^^)
'Programming > Python' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Python으로 Gmail 보내기 (7) | 2023.06.25 |
|---|---|
| Python BoilerPlate (파이썬 상용구) (0) | 2023.06.25 |
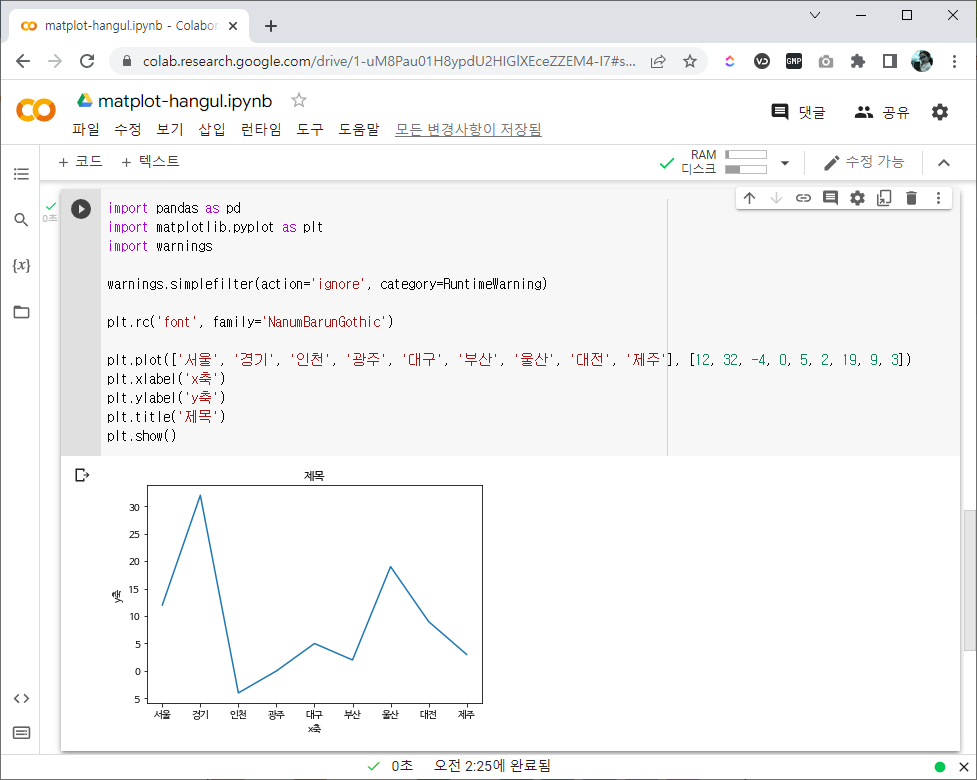
| matplotlib에서 한글 폰트 출력하기 (colab, local) (0) | 2022.07.18 |
| Ubuntu에서 Jupyter Notebook 설치하기 (1) | 2022.07.17 |
| Python으로 카카오톡 메시지 보내기 #1 (0) | 2022.07.16 |